10/20/2025. You've probably noticed that solving CAPTCHAs has become more frustrating than ever, yet bots seem to slip through anyway. The reality is that traditional verification methods are failing spectacularly in 2025, with AI-powered bots now able to solve many CAPTCHA puzzles with over 90% accuracy, while legitimate users waste precious seconds on distorted images and complex challenges. Fortunately, the future lies in
invisible verification systems that work silently in the background, analyzing behavioral patterns to distinguish humans from bots without any user friction. This shift from annoying puzzles to smooth protection is a massive evolution in web security.
TLDR:
- Traditional CAPTCHAs fail against modern AI bots that solve many of the CAPTCHA puzzles with 90%+ accuracy while users waste 35 seconds per challenge
- Invisible verification analyzes behavioral patterns like keystroke timing and mouse movements to detect bots without user friction
- Behavioral biometrics achieve 95%+ accuracy by identifying human imperfections that bots struggle to replicate authentically
- Continuous authentication monitors entire sessions rather than single checkpoints
- Roundtable delivers 87% bot detection accuracy through cognitive science research while maintaining complete user privacy
Why CAPTCHAs No Longer Work
Traditional CAPTCHAs are failing spectacularly in 2025. What once protected websites from simple bots now creates more problems than it solves. And the numbers tell a stark story:
users spend an average of 25 seconds solving CAPTCHA puzzles, creating what experts call a "friction tax" that drives away legitimate customers. Meanwhile, AI-powered fraud has evolved far beyond these outdated defenses.
Modern AI bots can solve many traditional CAPTCHAs with 90%+ accuracy while legitimate users struggle with distorted text and blurry images.
The accessibility crisis makes things worse. Visually impaired users face impossible challenges, while elderly users abandon transactions entirely when confronted with complex puzzles, creating legal compliance issues under ADA requirements.
But here's the real problem: sophisticated attackers have moved beyond simple automation. They're using machine learning models that excel at pattern recognition, making image-based challenges trivial to bypass. Bad bot traffic now represents nearly 50% of all web traffic, yet traditional verification methods catch only the most basic threats.
The result? A broken system that blocks humans while letting advanced bots through. Thankfully, the rise of instant human verification proposes to
put a stop to bad bot traffic while reducing the "friction tax" to zero.
The Rise of Invisible Verification
The future of human verification happens without users knowing it exists. Invisible verification systems work silently in the background, analyzing dozens of behavioral signals to distinguish humans from bots in real-time. Unlike traditional CAPTCHAs that interrupt user flow, invisible verification continuously monitors how people interact with websites. It tracks mouse movements, keystroke patterns, scrolling behavior, and timing variations that reveal cognitive signatures unique to humans.
The technology relies on a simple insight: humans are imperfect. We pause before typing, make micro-corrections with our mouse, and scroll with subtle irregularities that bots struggle to replicate authentically. Modern bot detection analyzes environmental factors as well. Device orientation changes, browser focus events, and even ambient light sensor data contribute to human verification scores. These passive signals create a complete behavioral fingerprint.
Some invisible verification systems can process over 100 behavioral signals per second without adding a single millisecond of latency to user interactions.
The shift toward invisibility reflects changing user expectations. People expect websites to work smoothly without friction. Advanced bot protection now happens at the infrastructure level, making security decisions before users even realize they're being verified. This approach inverts the traditional security model. Instead of challenging users to prove they're human, invisible systems assume legitimacy until behavioral patterns suggest otherwise. The result is frictionless security that protects without interrupting genuine user experiences.
How Behavioral Biometrics Work
Behavioral biometrics capture the unique ways humans interact with digital devices. Every keystroke, mouse movement, and screen touch creates a distinctive pattern that's nearly impossible for bots to replicate convincingly. And your typing rhythm reveals more than you think. Humans have inconsistent dwell times between keystrokes and varying pressure patterns that create unique signatures. We pause longer before certain letter combinations and type familiar words faster than complex ones. Mouse movements tell an even richer story. Humans make subtle course corrections, create curved paths, and exhibit micro-tremors that reflect our neurological processes. Bots typically move in perfectly straight lines or follow mathematically precise curves.
But behavioral biometrics also extend beyond desktop interactions. Mobile devices capture accelerometer data, touch pressure variations, and finger positioning that create additional verification layers. The way you hold your phone while scrolling is uniquely yours.
The technology of behavioral biometrics is based on cognitive psychology research which shows that human decision-making involves predictable delays and inconsistencies. Advanced behavioral analysis can detect when interactions lack the natural hesitation and error correction patterns that characterize authentic human behavior.
AI systems, such as those in
invisible verification solutions, learn these patterns through continuous observation. Machine learning models analyze thousands of interaction points to build behavioral profiles that distinguish human cognitive patterns from programmatic automation.
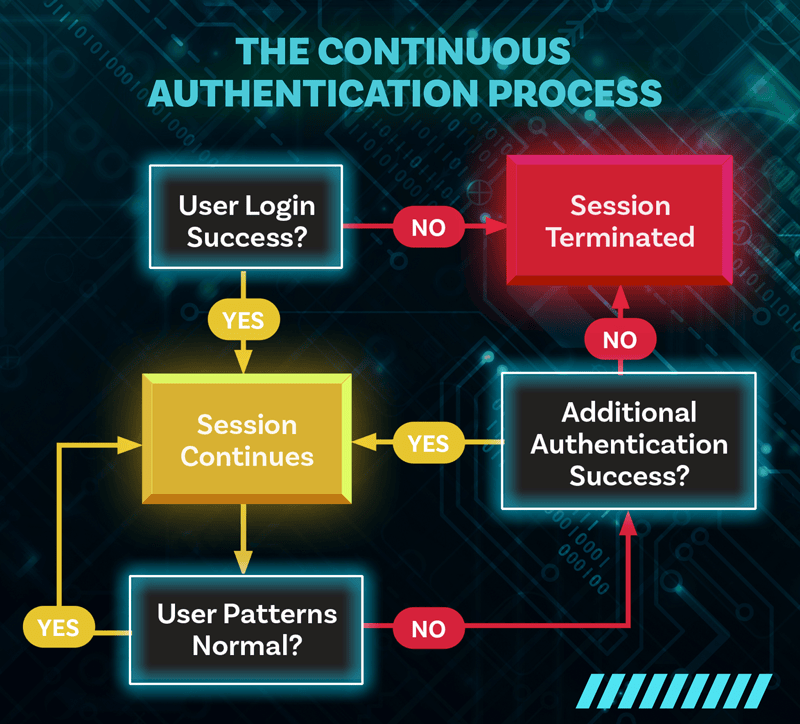
Continuous Authentication vs Discrete Verification
Traditional verification treats security as a single checkpoint. You solve a CAPTCHA, pass a test, then gain unrestricted access until your session expires. This binary approach creates massive security gaps. Continuous authentication, on the other hand, monitors user behavior throughout entire sessions. Instead of one verification moment, the system constantly checks whether the same human remains in control of the account. This matters because
account takeover attacks often happen mid-session. A legitimate user logs in, then an attacker hijacks their session through malware or credential theft. Discrete verification systems miss this transition entirely.
By contrast, instant human verification systems develop a behavioral baseline which adapts over time. If you typically type at 65 words per minute with specific pause patterns, sudden changes to 90 WPM with robotic consistency trigger risk alerts. The system learns your normal variations while flagging dramatic departures.
Next-generation fraud prevention relies on this persistent monitoring approach. Financial institutions use continuous authentication to protect high-value transactions even after initial login verification succeeds.
What makes this security technology so elegant is that the technical implementation runs invisibly. Users never experience additional friction, but security teams receive real-time alerts when behavioral patterns suggest account compromise or automated activity. This creates layered protection that evolves with threats rather than relying on static checkpoints which attackers only have to bypass once.
Privacy-First Human Verification
Privacy concerns have become the biggest barrier to user acceptance of verification systems. Traditional solutions often collect extensive personal data, track users across websites, and create detailed behavioral profiles that feel invasive.
Modern privacy-first verification takes a fundamentally different approach. Instead of harvesting personal information, these systems focus solely on interaction patterns that reveal human behavior without identifying individuals. You don't need to know who someone is to verify they're human. Behavioral signals like keystroke timing and mouse movement patterns provide sufficient verification without collecting names, emails, or tracking cookies.
GDPR compliance becomes straightforward when systems don't process personal data.
Biometric privacy trends show increasing regulatory focus on behavioral data collection, making privacy-by-design approaches important for global deployment. And transparency builds user trust. When verification systems explain their data practices clearly and show they're not building user profiles, adoption rates increase substantially. Users accept security measures that protect their privacy rather than exploit it.
That's why invisible verification technical architectures support privacy goals. Processing behavioral signals locally on devices, using ephemeral session data, and avoiding persistent identifiers creates invisible verification that respects user privacy while maintaining security effectiveness.
Industry Applications in October 2025
Financial services lead the adoption of invisible verification technology. Banks and lending institutions face sophisticated account takeover attempts where attackers use stolen credentials to access legitimate accounts. Traditional security measures miss these attacks because the login credentials are valid.
Behavioral fraud prevention now protects high-value transactions by monitoring user patterns throughout the entire session. When someone's typing rhythm suddenly changes during a wire transfer, the system flags potential account compromise.
E-commerce faces a different challenge: payment fraud and inventory manipulation. Bots create fake accounts, exploit promotional offers, and execute coordinated attacks during flash sales. Invisible verification identifies these automated behaviors before checkout completion.
Market research companies struggle with AI-generated survey responses that contaminate data quality.
Bot detection statistics show that up to 40% of online survey responses may be artificial, making research conclusions unreliable.
| Industry |
Primary Use Case |
Key Benefit |
Approximate Implementation Time |
| Financial Services |
Account Takeover Prevention |
Fraud Detection |
2 weeks |
| E-commerce |
Payment Protection |
Bot Detection |
1 week |
| Market Research |
Data Quality |
Improved human response rate |
3 days |
Healthcare applications protect patient portals from unauthorized access, while gaming companies prevent cheating and account farming. Each industry adapts continuous verification to handle specific threat patterns while maintaining user experience standards.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Deploying advanced verification systems creates technical hurdles that stop many organizations before they start. While there may be other challenges, the three biggest are legacy infrastructure, false positives, and performance impacts.
The solution to these challenges lies in phased deployment strategies. For example, start with low-risk applications to build confidence and expertise before protecting critical business functions. Then, use monitoring-only modes initially to understand baseline behavior patterns without blocking users. Just remember that successful implementations focus on gradual rollouts with continuous optimization rather than attempting full deployment immediately.
Moving Beyond Traditional CAPTCHA with Roundtable
CAPTCHAs were built for a simpler web, when threats were predictable and people had patience for puzzles. That world is gone. Automation is faster, users are busier, and tolerance for friction has vanished. The question is no longer whether CAPTCHAs work, but why we still rely on them at all.
Roundtable represents a different path forward. It treats verification not as an obstacle but as part of how people naturally interact online. Every movement, pause, and correction reveals the subtle unpredictability that defines human behavior. Roundtable reads that signal quietly, without interrupting flow.
Its promise lies in a simple idea: security should respect attention. Privacy is preserved through on-device processing, and accuracy remains high with 87% bot detection without collecting personal data or adding friction. It is protection that adapts to how people use the web today, not how they used it years ago.
The next generation of online trust will not come from stronger gates. It will come from systems that recognize humanity without demanding proof. Roundtable points toward that future, where verification fades from view and authenticity becomes part of the fabric of the web itself.
FAQ
How does invisible verification work without slowing down my website?
Invisible verification systems process behavioral signals in real-time without adding latency to user interactions, analyzing dozens of signals per second while maintaining zero friction for legitimate users.
What behavioral patterns can distinguish humans from bots?
Human behavioral patterns include keystroke timing irregularities, curved mouse movements with micro-corrections, natural scrolling variations, and cognitive delays that bots struggle to replicate authentically.
Can invisible verification detect account takeovers after login?
Yes, continuous authentication monitors behavioral patterns throughout entire sessions and can detect session hijacking within 5 seconds by identifying sudden changes in typing rhythm or interaction patterns.
How long does it take to implement behavioral biometric verification?
Most implementations take just a few hours depending on complexity, with simple API integrations requiring just minutes to deploy and providing immediate bot protection.
Final thoughts on choosing effective bot protection
The shift from annoying puzzles to smooth protection represents the biggest change in web security we've seen. You no longer need to frustrate users to stop bots when
invisible verification can analyze behavioral patterns silently in the background. Modern verification happens without users even knowing it exists, creating a better experience for everyone while catching threats that traditional methods miss completely.